The Informational functions evaluate the information of arguments.
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns True if the value of X is Boolean. If the value is not a Boolean, the function returns False.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=isbool(X)")
Example:
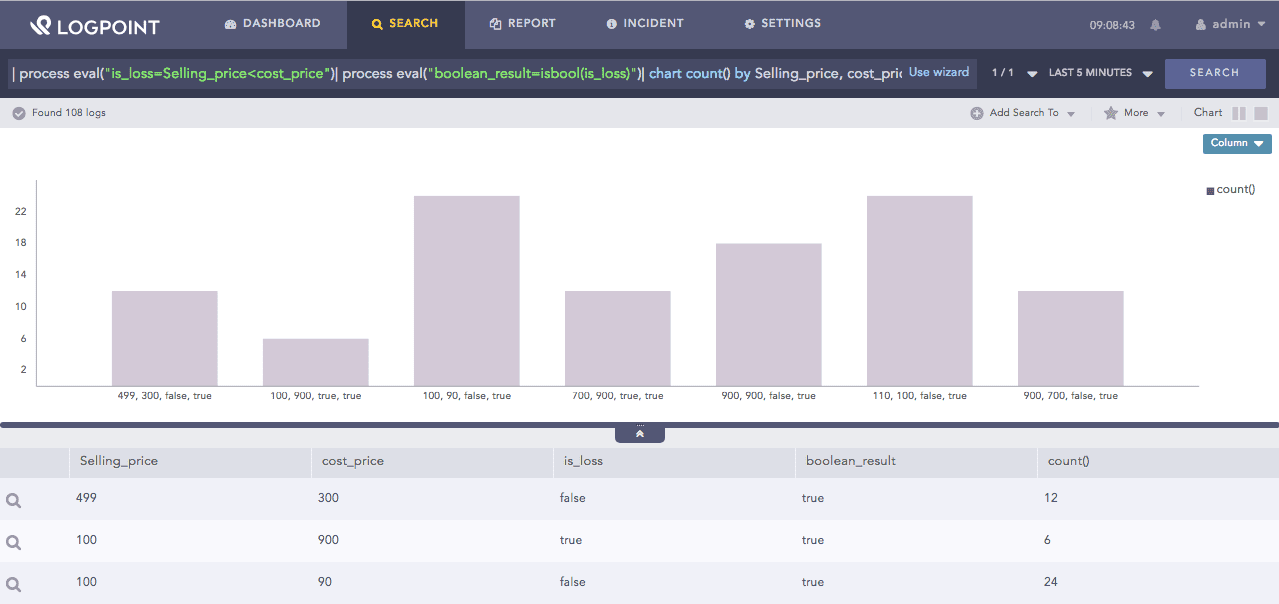
| process eval("is_loss=Selling_price<cost_price")
| process eval("boolean_result=isbool(is_loss)")
| chart count() by Selling_price, cost_price, is_loss, boolean_result
The above example first evaluates if the Selling_price is less than cost_price and returns its value in the is_loss identifier. Then, the isbol function returns true in the boolean_result identifier if the value in the is_loss field is Boolean. If the value is not a Boolean, the function returns False
The chart count() command displays the count of the combination of Selling_price, cost_price, is_loss, and boolean_result values as a chart and in a tabular form.
Isbool function¶
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns True if the value of X is an integer. If the value is not an integer, the function returns False.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=isint(X)")
Example:
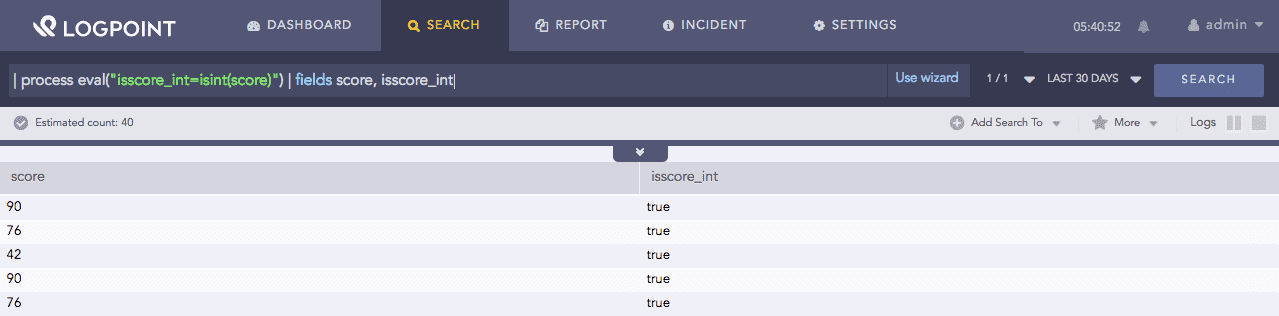
| process eval("isscore_int=isint(score)") | fields score, isscore_int
The above example returns true in the isscore_int identifier if the value in the score field is an integer. If the value is not an integer, the function returns False.
The fields command displays the value of score and isscore_int in a tabular form.
Isint function¶
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns True if the value of X is not null. If the value is null, the function returns False.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=isnotnull(X)")
Example:
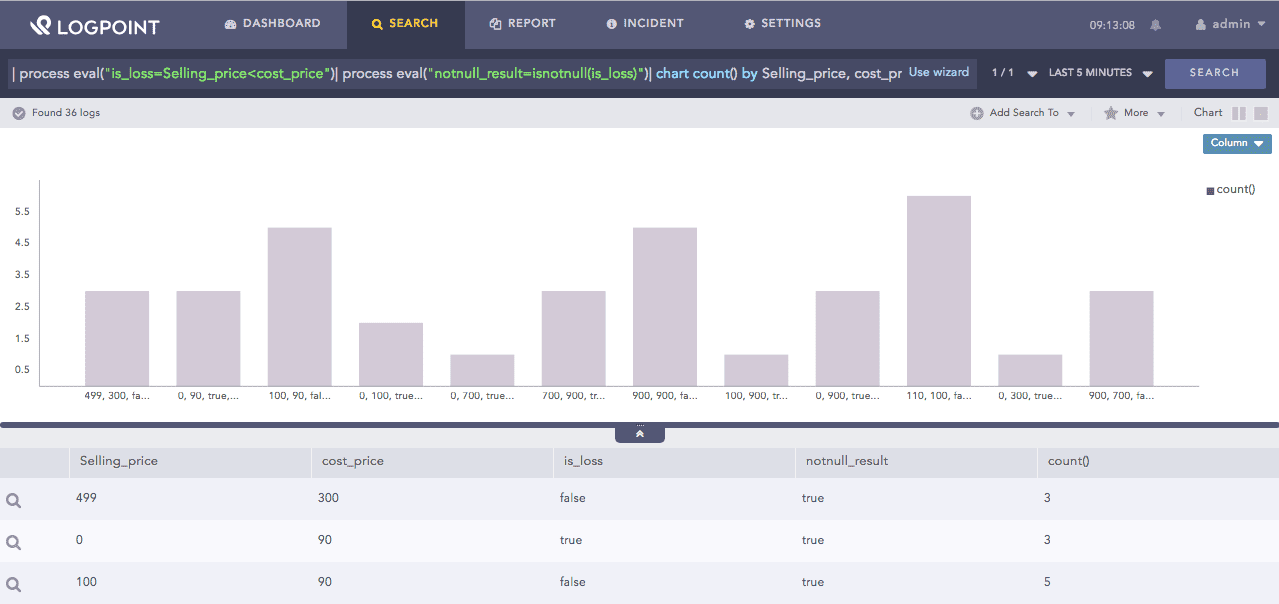
| process eval("is_loss=Selling_price<cost_price")
| process eval("notnull_result=isnotnull(is_loss)")
| chart count() by Selling_price, cost_price, is_loss, notnull_result
The above example first evaluates if the Selling_price is less than cost_price and returns its value in the is_loss identifier. Then, the isnotnull function returns true in the notnull_result identifier if the value in the is_loss field is not null. If the value is null, the function returns False.
The chart count() command displays the count of the combination of Selling_price, cost_price, is_loss, and notnull_result values as a chart and in a tabular form.
Isnotnull function¶
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns True if the value of X is null. If the value is not null, the function returns False.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=isnull(X)")
Example:
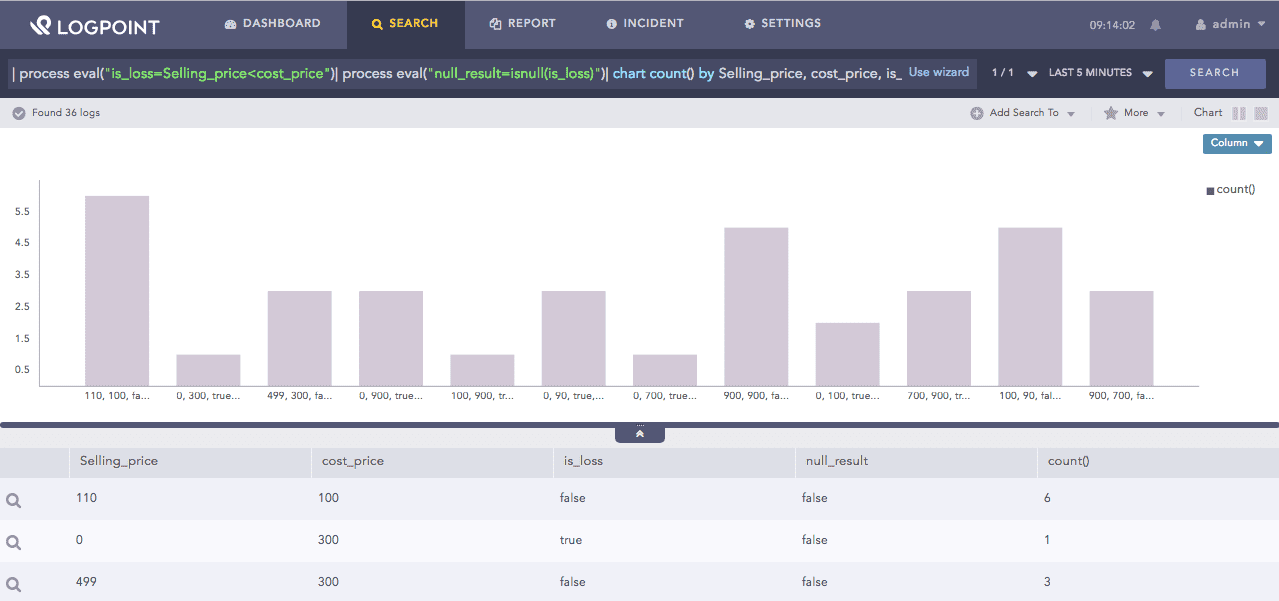
| process eval("is_loss=Selling_price<cost_price")
| process eval("null_result=isnull(is_loss)")
| chart count() by Selling_price, cost_price, is_loss, null_result
The above example first evaluates if the Selling_price is less than cost_price and returns its value in the is_loss identifier. Then, the isnull function returns true in the null_result identifier if the value in the is_loss field is null. If the value is not null, the function returns False.
The chart count() command displays the count of the combination of Selling_price, cost_price, is_loss, and null_result values as a chart and in a tabular form.
Isnull function¶
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns True if the value of X is a number. If the value is not a number, the function returns False.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=isnum(X)")
Example:
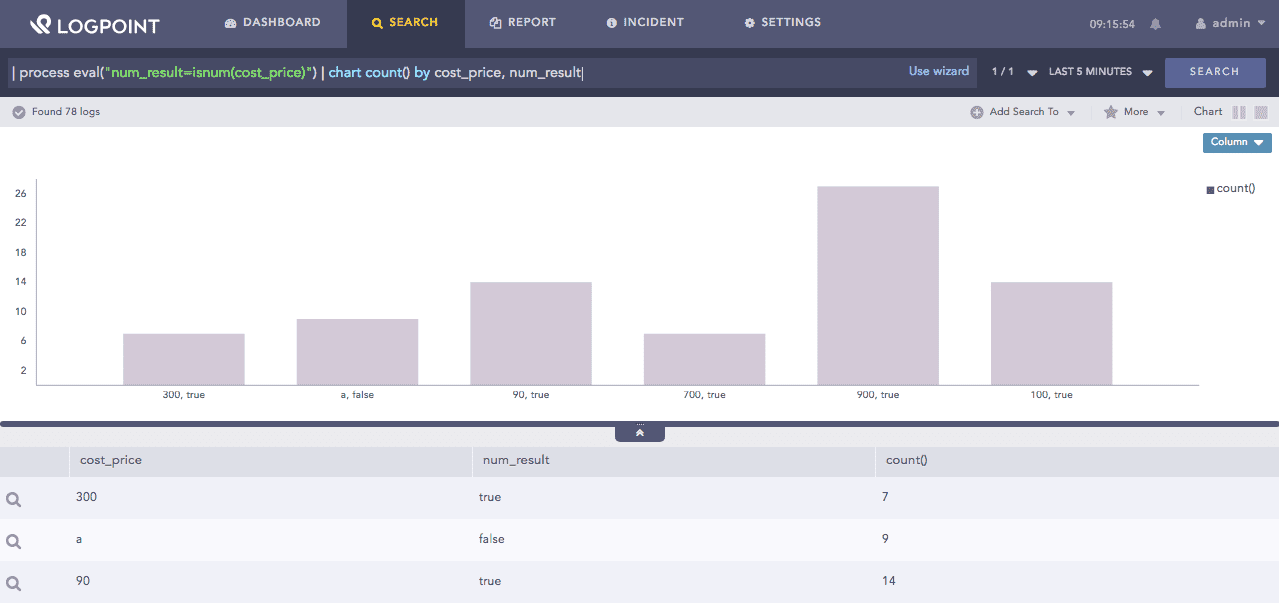
| process eval("num_result=isnum(cost_price)") | chart count() by cost_price, num_result
The above example returns true in the num_result identifier if the value in the score field is a number. If the value is not a number, the function returns False.
The chart count() command displays the count of the combination of cost_price and num_result values as a chart and in a tabular form.
Isnum function¶
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns True if the value of X is a string. If the value is not a string, the function returns False.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=isstr(X)")
Example:
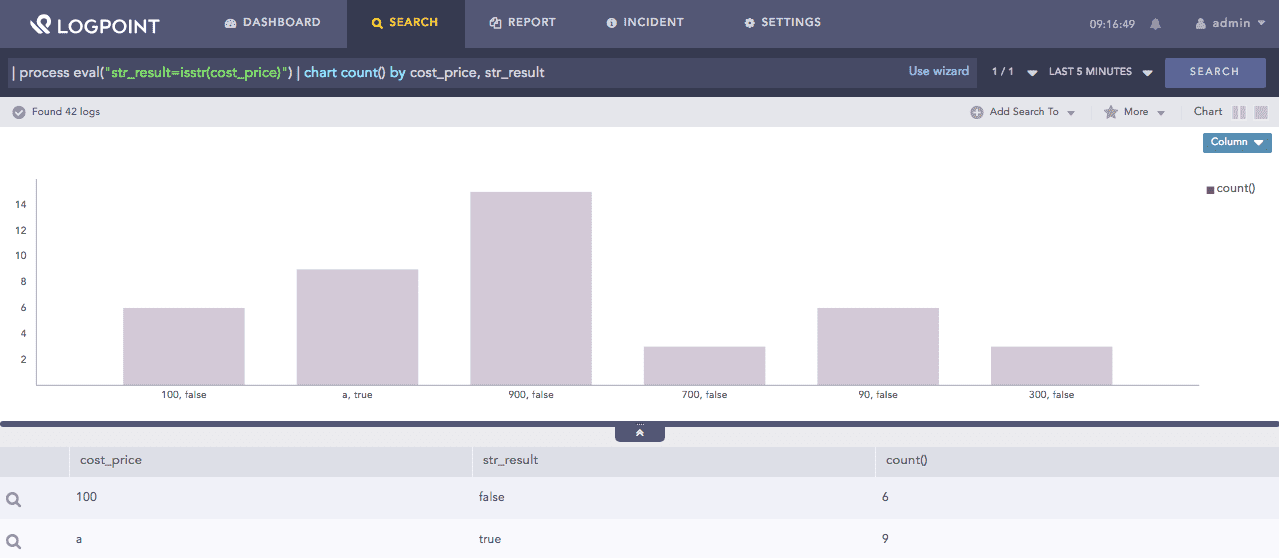
| process eval("str_result=isstr(cost_price)") | chart count() by cost_price, str_result
The above example returns true in the str_result identifier if the value in the cost_price field is a string. If the value is not a string, the function returns False.
The chart count() command displays the count of the combination of cost_price and str_result values as a chart and in a tabular form.
Isstr function¶
This function accepts one argument X as input and returns the field type of the value of X, such as integer, double, string and boolean.
Syntax:
| process eval("identifier=typeof(X)")
Example:
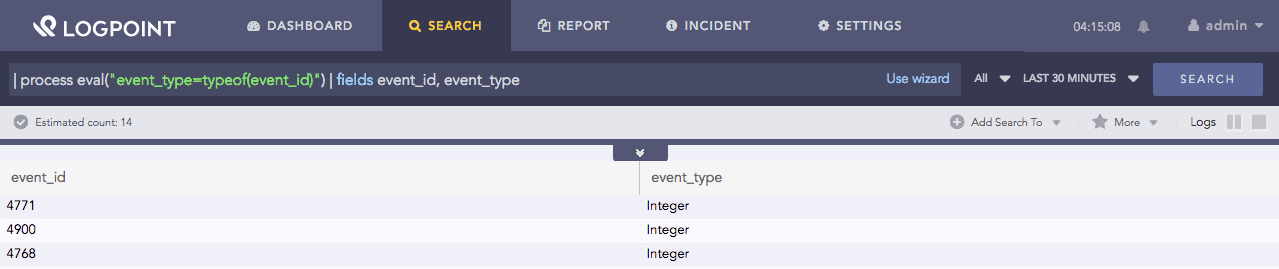
| process eval("event_type=typeof(event_id)") | fields event_id, event_type
The above example returns the field type of the event_id value in the event_type identifier.
The fields command displays the value of event_id and event_type in a tabular form.
Typeof function¶
We are glad this guide helped.
Please don't include any personal information in your comment
Contact Support